A sad reality
In general, the surface of the seasonal pack ice reached 16.5 million km2. However, since 1979, it has been decreasing day by day. In March 2013, the surface of the ice pack was only 15 million km2. [1]
The ice pack, more important than we think
To begin with, it should be noted that in the Arctic, every winter, the polar night allows a cooling of the atmosphere and also of the surface layer of the ocean. In fact, when the temperature of the ocean surface reaches -1.8°C, the ocean starts to freeze and this is how the ice pack is formed. This seasonal increase of the pack ice occurs during the month of March and can reach 15 or even 16 million km2. As for the thickness, it can range from a few centimeters to about 2 meters in height. [1]
But what is most important, is the role of this ice pack. Indeed, this ice cover has a very important impact on the climatic balance of the Northern Hemisphere as well as on ocean circulation. It is this ice cover that will limit the exchanges between the atmosphere and the ocean while reflecting a large part of the solar radiation during the spring. The ice pack is also a place where polar bears, ringed seals, Inuit, etc. [1]

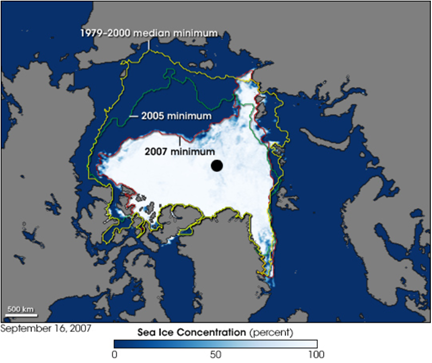
A frightening decrease
Seasonal Arctic sea ice does indeed melt in the spring and this in a natural way. After that, only the “perennial” pack ice remains, which is composed of multi-year ice that can be several meters thick. The extension of this so-called “perennial” ice pack is in autumn, during the month of September. The abnormal melting of this perennial pack ice began in 1979. [1]
Indeed, in September 1979, the perennial pack ice reached 8 million km2. Then, the more the years passed, the more the surface of this ice pack decreased. In 2013 it reached 5.1 million km2. In 2012, more than 3.4 million km2. In 34 years, the oldest and oldest ice, decreased drastically from 30% to 5%. Moreover, when the surface of perennial pack ice decreases, it is also its thickness that decreases but also its volume. As a result, the ice pack becomes accessible to global warming. [1]
This melting of the ice pack is also happening on the Antarctic side. Indeed, this ice was quite stable. From 2012 to 2014, it has even expanded a little. However, it is during the year 2015 that the ice started to melt and this in a rather fast way. Indeed, during the southern summer of 2018-2019, its surface was reduced by half or even more. [2]
Ice is melting, global warming is increasing
According to Sam Carana, an anonymous group of climatologists, the melting ice from the Southern Ocean is now causing warming that has become comparable to that due to human emissions. But that’s not all. In fact, if we add the collapse of the Arctic Ocean ice, the warming caused by the darkening of the Earth, becomes higher than that of human emissions! This is why the temperatures of recent years have been so high compared to normal. Melting ice is accelerating global warming in an aggressive way. This is why we must act now. [2]

References:
[1]: Taverniers, P. (2015, avril 29). Fonte de la banquise—Réchauffement climatique. Grands Espaces. https://www.grands-espaces.com/nature/fonte-de-la-banquise-rechauffement-climatique-grands-espaces/
[2]: Retelska, D. (2019, août 6). La fonte des banquises accélère le réchauffement climatique et en devient le facteur principal. Le climat aujourd’hui et demain. https://blogs.letemps.ch/dorota-retelska/2019/08/06/la-fonte-des-banquises-accelere-le-rechauffement-climatique-et-en-devient-le-facteur-principal/
[3]: TdG. (2020, août 18). Climat – En Arctique, la banquise fond plus vite que prévu. Tribune de Genève. https://www.tdg.ch/en-arctique-la-banquise-fond-plus-vite-que-prevu-235049703128




